
Computer number system
Computer number system
In computers, the main numeral systems are based on the positional system in base 2 (binary numeral system), with two binary digits, 0 and 1. Positional systems obtained by grouping binary digits by three (octal numeral system) or four (hexadecimal numeral system) are commonly used.
The technique to represent and work with numbers is called number system. Decimal number system is the most common number system. Other popular number systems include binary number system, octal number system, hexadecimal number system, etc.
Decimal Number system
Decimal number system is a base 10 number system having 10 digits from 0 to 9. This means that any numerical quantity can be represented using these 10 digits. Decimal number system is also a positional value system. This means that the value of digits will depend on its position. Let us take an example to understand this.
Say we have three numbers – 734, 971 and 207. The value of 7 in all three numbers is different−
➡️ In 734, value of 7 is 7 hundreds or 700 or 7 × 100 or 7 × 102
➡️ In 971, value of 7 is 7 tens or 70 or 7 × 10 or 7 × 101
➡️ In 207, value 0f 7 is 7 units or 7 or 7 × 1 or 7 × 100
The weightage of each position can be represented as follows −
| 10⁵ | 10⁴ | 10³ | 10² | 10¹ | 10⁰ |
Decimal Number System
In digital systems, instructions are given through electric signals; variation is done by varying the voltage of the signal. Having 10 different voltages to implement decimal number system in digital equipment is difficult. So, many number systems that are easier to implement digitally have been developed. Let’s look at them in detail.
Binary Number system
The easiest way to vary instructions through electric signals is two-state system – on and off. On is represented as 1 and off as 0, though 0 is not actually no signal but signal at a lower voltage. The number system having just these two digits – 0 and 1 – is called binary number system.
Each binary digit is also called a bit. Binary number system is also positional value system, where each digit has a value expressed in powers of 2, as displayed here.
Binary Number System
In any binary number, the rightmost digit is called least significant bit (LSB) and leftmost digit is called most significant bit (MSB).
MSB lsb
And decimal equivalent of this number is sum of product of each digit with its positional value.
110102 = 1×24 + 1×23 + 0×22 + 1×21 + 0×20
= 16 + 8 + 0 + 2 + 0
= 2610
Computer memory is measured in terms of how many bits it can store. Here is a chart for memory capacity conversion.
1 byte (B) = 8 bits
1 Kilobytes (KB) = 1024 bytes
1 Megabyte (MB) = 1024 KB
1 Gigabyte (GB) = 1024 MB
1 Terabyte (TB) = 1024 GB
1 Exabyte (EB) = 1024 PB
1 Zettabyte = 1024 EB
1 Yottabyte (YB) = 1024 ZB
Octal Number System
Octal Number System
Characteristics of the octal number system are as follows −
Uses eight digits, 0,1,2,3,4,5,6,7
Also called as base 8 number system
Each position in an octal number represents a 0 power of the base (8). Example 80
Last position in an octal number represents a x power of the base (8). Example 8x where x represents the last position – 1
For example
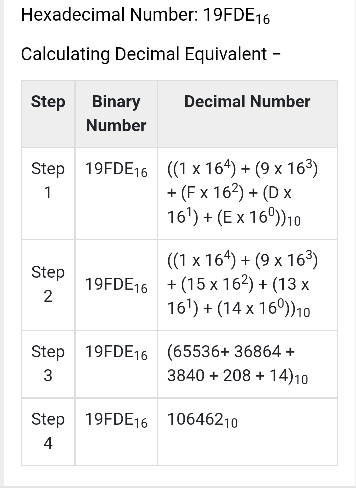
Hexa Decimal Number System
Characteristics of hexadecimal number system are as follows −
Uses 10 digits and 6 letters, 0, 1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6, 7, 8, 9, A, B, C, D, E, F
Letters represent the numbers starting from 10. A = 10. B = 11, C = 12, D = 13, E = 14, F = 15
Also called as base 16 number system
Each position in a hexadecimal number represents a 0 power of the base (16). Example, 160
Last position in a hexadecimal number represents a x power of the base (16). Example 16x where x represents the last position – 1
Example

Design by Ayush Vishwakarma computer student full support my computer teacher ‘Dear’ Basant sir